|
LA DISSEZIONE ACUTA DELL’ AORTA: EPIDEMIOLOGIA E CLINICA
Eduardo Bossone e Rodolfo Citro (*) U.O. Utic-Cardiologia Ospedale di Cava dei Tirreni (*) ASL SA 3 Vallo della Lucania Dipartimento Cardiovascolare U.O. Utic-Cardiologia Ospedale San Luca Vallo della Lucania
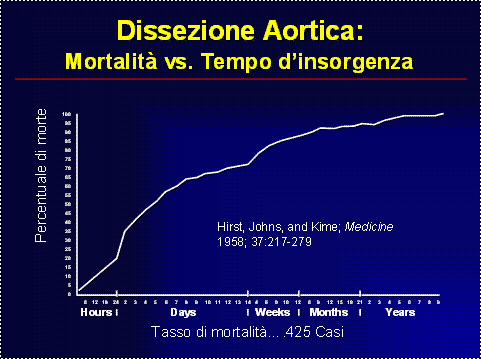
La Dissezione Aortica Acuta (DAA) e’ una rara ma catastrofica emergenza cardiovascolare con una elevata mortalitÓ se non appropriatamente trattata.
Essa si verifica con una frequenza di almeno 2000 casi all’ anno negli USA. Ha una prevalenza di 0.5 – 2.95 /100000/anno con la pi¨ alta frequenza in Italia 4.04 /100000/anno. Sono tre i sistemi di classificazione utilizzati per la AAD: DeBakey: Tipo I-II-III, Stanford: Tipo A e B, Descrittivo: prossimale e distale. Esse riflettono la sede e l’ estensione del coinvolgimento aortico e si basano sullo stesso principio: distinguono le dissezioni aortiche con o senza l’ interessamento dell’ aorta
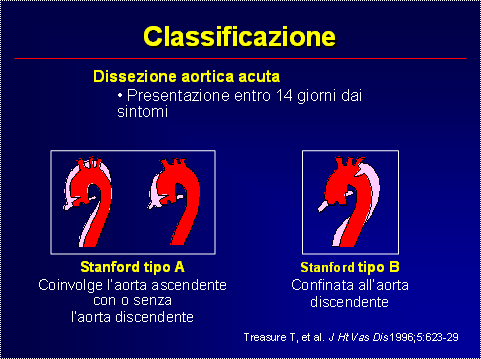
Classificazione della sindrome aortica acuta
Classificazione secondo Standford Tipo A: dissezione dell’aorta ascendente con o senza l’ interessamento dell’ aorta discendente Tipo B: dissezione soltanto dell’aorta discendente. Classificazione secondo De Bakey Tipo 1: dissezione dell’intera aorta Tipo 2: dissezione aorta ascendente Tipo 3: dissezione dell’aorta discendente Nuova Classificazione ESC Classe 1: classica dissezione aortica con presenza di flap tra vero e falso lume Classe 2: distruzione della media con formazione di ematoma/emorragia intramurale Classe 3: minima dissezione senza ematoma e con espansione eccentrica in corrispondenza della lesione Classe 4: rottura di placca aterosclerotica con formazione di ulcerazione, ulcera penetrante con ematoma perilesionale, usualmente sottoavventiziale. Classe 5: dissezione iatrogena e traumatica
Modified from: Erbel R, Alfonso F, Boileau C, et al. Diagnosis and management of aortic dissection: task force report of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur Heart J. 2001; 22: 1642–1681
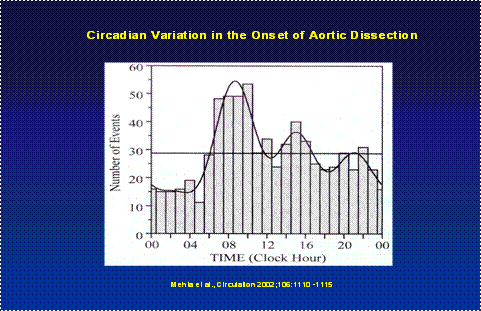
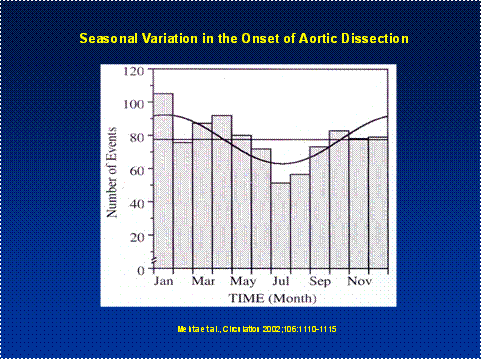
In linea con altre patologie cardiovascolari (infarto del miocardio, stroke, ipertensione arteriosa) la DAA esibisce un ritmo circadiano e circannuale. Essa infatti Ŕ piu’ frequente di mattina e durante l’ inverno.
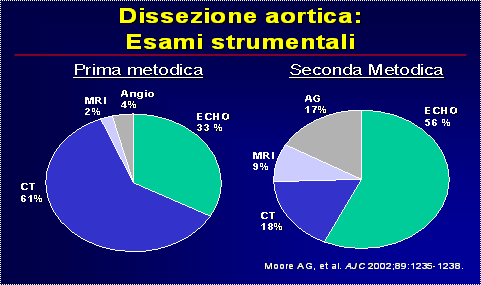
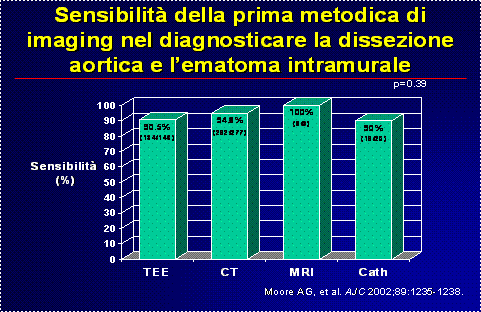
Per la non specificitÓ dei sintomi e segni la diagnosi resta difficile. Quindi risulta indispensabile un elevato sospetto clinico seguito da un test di imaging: ecocardiografia transesofagea, tomografia assiale computerizzata, risonanza magnetica nucleare, aortografia. Esse hanno tutte un’alta sensibilitÓ e specificitÓ anche se la TAC Ŕ la pi¨ utilizzata seguita dalla TEE.
E’da sottolineare che nonostante i notevoli progressi in termini di tecniche diagnostiche e terapeutiche (mediche, endovascolari e chirurgiche), la mortalitÓ della DAA resta comunque elevata. Anche dopo un efficace “definitivo” trattamento della DAA, i pazienti rimangono ad un considerevole rischio di successive dissezioni, aneurismi e rotture dell’ aorta. Sono, quindi, necessari controlli clinici e diagnostici seriati.
Tab. I. Late complications of aortic valve dissection and follow-up evaluation.
Modified from: Erbel R, Alfonso F, Boileau C, et al. Diagnosis and management of aortic dissection: task force report of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur Heart J. 2001; 22: 1642–1681; Isselbacher EM. Aortic dissection in Atlas of Vascular Disease, Creager MA Second Edition (Series Editor Braunwald E); Current Medicine LLC, Philadelphia, PA, USA 2003, 24-43.
1. Erbel R, Alfonso F, Boileau C, Dirsch O, Eber B, Haverich A, Rakowski H, Struyven J, Radegran K, Sechtem U, Taylor J, Zollikofer C, Klein WW, Mulder B, Providencia LA. Diagnosis and management of aortic dissection: task force report of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur Heart J 2001; 22:1642–1681. 2. Hagan PG, Nienaber CA, Isselbacher EM, Bruckman D, Karavite DJ, Russman PL, Evangelista A, Fattori R, Suzuki T, Oh JK, Moore AG, Malouf JF, Pape LA, Gaca C, Sechtem U, Lenferink S, Deutsch HJ, Diedrichs H, Marcos y Robles J, Llovet A, Gilon D, Das SK, Armstrong WF, Deeb GM, Eagle KA. The International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection (IRAD): new insights into an old disease. JAMA 2000;283:897-903. 3. Mehta RH, Suzuki T, Hagan PG, Bossone E, Gilon D, Llovet A, Maroto LC, Cooper JV, Smith DE, Armstrong WF, Nienaber CA, Eagle KA. Predicting death in patients with acute type A aortic dissection. Circulation 2002;105:200-206. 4. Erbel R, Oelert H, Meyer J, Puth M, Mohr-Katoly S, Hausmann D, Daniel W, Maffei S, Caruso A, Covino FE, Dialetto G, Iacono C, Cotrufo M, Baroni M, Terrazzi M, Fraser A, Taams M, Slavich G, Sutherland G, Roelandt J, Marcaggi X. Effect of medical and surgical therapy on aortic dissection evaluated by transesophageal echocardiography. Implications for prognosis and therapy. Circulation 1993;87:1604–15. 5. Hirst AE Jr, Johns VJ Jr, Kime SW Jr. Dissecting aneurysm of the aorta: a review of 505 cases. Medicine 1958; 37: 217-279. 6. Doroghazi RM, Slater EE, DeSanctis RW, Buckley MJ, Austen WG, Rosenthal S. Long-term survival of patients with treated aortic dissection. J Am Coll Cardiol 1984; 3:1026–1034. 7. Mehta RH, O'Gara PT, Bossone E, Nienaber CA, Myrmel T, Cooper JV, Smith DE, Armstrong WF, Isselbacher EM, Pape LA, Eagle KA, Gilon D. Acute type A aortic dissection in the elderly: clinical characteristics, management, and outcomes in the current era. J Am Coll Cardiol 2002;40:685-692. 8. Bossone E, Rampoldi V, Nienaber CA, Trimarchi S, Ballotta A, Cooper JV, Smith DE, Eagle KA, Mehta RH. Usefulness of pulse deficit to predict in-hospital complications and mortality in patients with acute type A aortic dissection. Am J Cardiol 2002;89:851-5. 9. Erbel R, Engberding R, Daniel W, Roelandt J, Visser C, Rennollet H. Echocardiography in diagnosis of aortic dissection. Lancet 1989;1:457-61. 10. Nienaber CA, von Kodolitsch Y, Nicolas V, Siglow V, Piepho A, Brockhoff C, Koschyk DH, Spielmann RP. The diagnosis of thoracic aortic dissection by noninvasive imaging procedures. N Engl J Med 1993;7;328:1-9. 11. Cigarroa JE, Isselbacher EM, DeSanctis RW, Eagle KA. Diagnostic imaging in the evaluation of suspected aortic dissection. Old standards and new directions. N Engl J Med 1993;328:35-43. 12. Keren A, Kim CB, Hu BS, Eyngorina I, Billingham ME, Mitchell RS, Miller DC, Popp RL, Schnittger I. Accuracy of biplane and multiplane transesophageal echocardiography in diagnosis of typical acute aortic dissection and intramural hematoma. J Am Coll Cardiol 1996;28:627-36. 13. Moore AG, Eagle KA, Bruckman D, Moon BS, Malouf JF, Fattori R, Evangelista A, Isselbacher EM, Suzuki T, Nienaber CA, Gilon D, Oh JK. Choice of computed tomography, transesophageal echocardiography, magnetic resonance imaging, and aortography in acute aortic dissection: International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection (IRAD). Am J Cardiol 2002;89:1235-38. 14. Armstrong WF, Bach DS, Carey L, Chen T, Donovan C, Falcone RA, Marcovitz PA. Spectrum of acute dissection of the ascending aorta: a transesophageal echocardiographic study. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 1996;9:646-56. 15. Ballal RS, Gatewood RP Jr, Nanda NC, Sanyal RS, Kirklin JK, Pacifico AD. Usefulness of transesophageal Echocardiography in assessment of aortic dissection. Circulation 1991;84:1903-1914. 16. Chan KL. Usefulness of transesophageal echocardiography in the diagnosis of conditions mimicking aortic dissection. Am Heart J 1991;122:495-504.
17.
Armstrong WF, Bach DS, Carey LM, Froehlich J, Lowell M,
Kazerooni EA. Clinical and echocardiographic findings in
patients with suspected acute aortic dissection. 18. Tsai TT, Bossone E, Isselbacher EM, Nienaber CA, Evangelista A, Fang J, Smith DE, Cooper JV, Hutchison S, O'Gara P, Eagle KA, Mehta RH Clinical characteristics of hypotension in patients with acute aortic dissection. Am J Cardiol. 2005 Jan 1;95(1):48-52. 19. Ergin MA, Phillips RA, Galla JD, Lansman SL, Mendelson DS, Quintana CS, Griepp RB. Significance of distal false lumen after Type A dissection repair. Ann Thorac Surg 1994;57: 820–25. 20. Bossone E, Tsai TT, Eagle KA, Fattori R, Trimarchi S, Cooper JV, Isselbacher E, Nienaber C. Characterization of medically managed patients with acute type A aortic dissection:: insignts from the international registry of acute aortic dissection (IRAD).World Congress of Cardiology Barcelona, Spain 2006. 21. Trimarchi S, Nienaber CA, Rampoldi V, Myrmel T, Suzuki T, Bossone E, Tolva V, Deeb MG, Upchurch GR Jr, Cooper JV, Fang J, Isselbacher EM, Sundt TM 3rd, Eagle KA. Role and results of surgery in acute type B aortic dissection: insights from the International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection (IRAD).Trimarchi S, Nienaber CA, Rampoldi V, Myrmel T, Suzuki T, Bossone E, Tolva V, Deeb MG, Upchurch GR Jr, Cooper JV, Fang J, Isselbacher EM, Sundt TM 3rd, Eagle KA. Circulation. 2006 Jul 4;114(1 Suppl):I357-64. 22. Sangiorgi G, Trimarchi S, Mauriello A, Righini P, Bossone E, Suzuki T, Rampoldi V, Eagle KA. Plasma levels of metalloproteinases-9 and -2 in the acute and subacute phases of type A and type B aortic dissection. Cardiovasc Med 2006 May;7(5):307-315.
23.
Mehta RH, Manfredini R, Bossone E, Fattori R, Evagelista
A, Boari B, Cooper JV, Sechtem U, Isselbacher EM, Nienaber CA,
Eagle KA; International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection
(IRAD) Investigators.
The
winter peak in the occurrence of acute aortic dissection is
independent of climate. 24. Mehta RH, Manfredini R, Bossone E, Hutchison S, Evangelista A, Boari B, Cooper JV, Smith DE, O'Gara PT, Gilon D, Pape LA, Nienaber CA, Isselbacher EM, Eagle KA. Does circadian and seasonal variation in occurrence of acute aortic dissection influence in-hospital outcomes? Chronobiol Int. 2005;22(2):343-51. 25. Manfredini R, Boari B, Gallerani M, Salmi R, Bossone E, Distante A, Eagle KA, Mehta RH.Chronobiology of rupture and dissection of aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 2005 Apr;41(4):736-7.
26.
Trimarchi S, Nienaber CA, Rampoldi V, Myrmel T, Suzuki T,
Mehta RH, Bossone E, Cooper JV, Smith DE, Menicanti L, Frigiola
A, Oh JK, Deeb MG, Isselbacher EM, Eagle KA. Contemporary
results of surgery in acute type A aortic dissection: The
International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissectionexperience.
27.
Beckman JA, Mehta RH, Isselbacher EM, Bossone E, Cooper
JV, Smith DE, Fang J, Sechtem U, Pape LA, Myrmel T, Nienaber CA,
Eagle KA, O'Gara PT. Branch vessel complications are increased
in aortic dissection patients with renal insufficiency. 28. Collins JS, Evangelista A, Nienaber CA, Bossone E, Fang J, Cooper JV, Smith DE, O'Gara PT, Myrmel T, Gilon D, Isselbacher EM, Penn M, Pape LA, Eagle KA, Mehta RH; International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection (IRAD). Differences in clinical presentation, management, and outcomes of acute type a aortic dissection in patients with and without previous cardiac surgery. Circulation. 2004 Sep 14;110 (11 Suppl 1):II237-42. 29. Manfredini R, Boari B, Gallerani M, Salmi R, Bossone E, Distante A, Eagle KA, Mehta RH. Chronobiology of rupture and dissection of aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg. 2004 Aug;40(2):382-8. 30. Januzzi JL, Marayati F, Mehta RH, Cooper JV, O'Gara PT, Sechtem U, Bossone E, Evangelista A, Oh JK, Nienaber CA, Eagle KA, Isselbacher EM. Comparison of aortic dissection in patients with and without Marfan's syndrome (results from the International Registry of Aortic Dissection). Am J Cardiol. 2004 Aug.
31.
Nienaber CA, Fattori R, Mehta RH, Richartz BM,
Evangelista A, Petzsch M, Cooper JV, Januzzi JL, Ince H, Sechtem
U, Bossone E, Fang J, Smith DE, Isselbacher EM, Pape LA, Eagle
KA; International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection.
Gender-related differences in acute aortic dissection. 32. Mehta RH, Bossone E, Evangelista A, O'Gara PT, Smith DE, Cooper JV, Oh JK, Januzzi JL, Hutchison S, Gilon D, Pape LA, Nienaber CA, Isselbacher EM, Eagle KA. International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection Investigators. Acute type B aortic dissection in elderly patients: clinical features, outcomes, and simple risk stratification rule. Ann Thorac Surg. 2004 May;77(5):1622-8; discussion 1629. 33. Suzuki T, Mehta RH, Ince H, Nagai R, Sakomura Y, Weber F, Sumiyoshi T, Bossone E, Trimarchi S, Cooper JV, Smith DE, Isselbacher EM, Eagle KA, Nienaber CA; International Registry of Aortic Dissection. Clinical profiles and outcomes of acute type B aortic dissection in the current era: lessons from the International Registry of Aortic Dissection (IRAD). Circulation. 2003 Sep 9;108 Suppl 1:II312-7. 34. Nallamothu BK, Mehta RH, Saint S Llovet A, Bossone E, Cooper JV, Sechtem U, Isselbacher EM, Nienaber CA, Eagle KA, Evangelista A. Syncope in acute aortic dissection: diagnostic, prognostic, and clinical implications. Am J Med 2002 Oct 15; 113(6):468-71. 35. Mehta RH, O’ Gara PT, Bossone E, Nienaber CA, Myrmel T, Cooper JV, Smith DE, Armstrong WF, Isselbacher EM, Pape LA, Eagle Kal. Acute type A aortic dissection in the elderly: clinical characteristics, management, and outcome in the current era. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002 Aug 21 ;40 (4):685-92. 36. Mehta RH, Manfredini R, Hassan F, Sechtem U, Bossone E, Oh JK, Cooper JV, Smith DE, Portaluppi F, Penn M, Hutchison S, Nienaber CA, Isselbacher EM, Eagle KA. Chronobiological patterns of acute aortic dissection. Circulation. 2002, Aug 27; 106 (9): 1110-5.
|